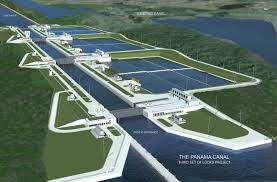
The Panama Canal Expansion or the third set of locks project is undoubtedly one of the largest and more important infrastructural projects of the twenty first century. This challenging task was to increase the capacity and efficiency of this 100-year old canal that holds a strategic importance in international maritime transportation.
Except for the old Suez Canal that connects the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea, the only main canal that created a shortcut in intercontinental sea transport was the Panama Canal that begun in 1914. However, they were limited by the ability to handle newer ships that came with the growth in international trade and larger ships. This led to the development of the expansion project aimed at enabling the passage of New Panamax vessels which are even bigger than the old Panamax category.

Project Scope
It aimed to expand a Panama Canal by constructing new locks on the Atlantic and the Pacific sides with addition of an extra lockage way for ships. These include the new locks, which have a dimension of 427 meters in length, 55 meters in breadth and 18 meters in height. In depth of 3 metre, it will be able to accommodate vessel up to L365m
It also included the elongation and widening of the current channels, alongside the creation of consumption channels of access. Moreover, advancements were also made to the extensions of the Gatun Lake and the canals governing the traffic also based on the increasing traffic and large size of the ships present.
Timeline and Cost
The expansion project was inaugurated in September 2007 at a cost of about $ 5. 25 billion. The construction phase of the project was estimated to take about eight years to be completed. However, the execution of the project was hampered by many issues of delay and high costs such as technical complexities, problems with the labour unions and contractual disputes.
However, these challenges did not deter the expansion of the canal that was finally completed and inaugurated on 26th June 2016. Thus, the overall cost of the construction has been estimated to cost around $5 when completed. 5 billion.

Economic and Environmental Impact
The Panama Canal Expansions has ultimately affected the flow of commodities around the world. In this way, it has enlarged and improved the canal to admit more carrier ships making the transit shorter and cheaper for many routes. This has especially favored Asian exports to the East Coast of the United States, which had been done before through routes that went South round the horn of South America or through the Suez Canal, the latter being time-consuming and expensive.
The new canal has social benefits as it has helped Panama to increase the revenue from tolls and other services that are related to the operations of the canal and are key contributors to the GDP of Panama. It has also generated thousands of employment opportunities, not only when the project was still under construction but also those which are continuously being offered now.
However, such expansion has caused some environmental issues which are discussed below;Some of the problems that have been connected to the construction and increased traffic include water use issues since the canal requires large quantities of fresh water from Gatun Lake. Some measures have been taken in order to reduce the dangerous effects; for instance, the new locks are equipped with water-saving basins.
Scope
The innovative and expanded Panama canal demonstrates the history of the modern improvement and addition of globalization, Due to progress of international trade and transport, the widened canal will assume the characteristics of a transport facility and as a means of directly exercising influence on the development of transport and commerce and trade in the various parts of the world.
Read also The biggest malls in America
Read also Top 10 Largest Airports in North America by Land Area