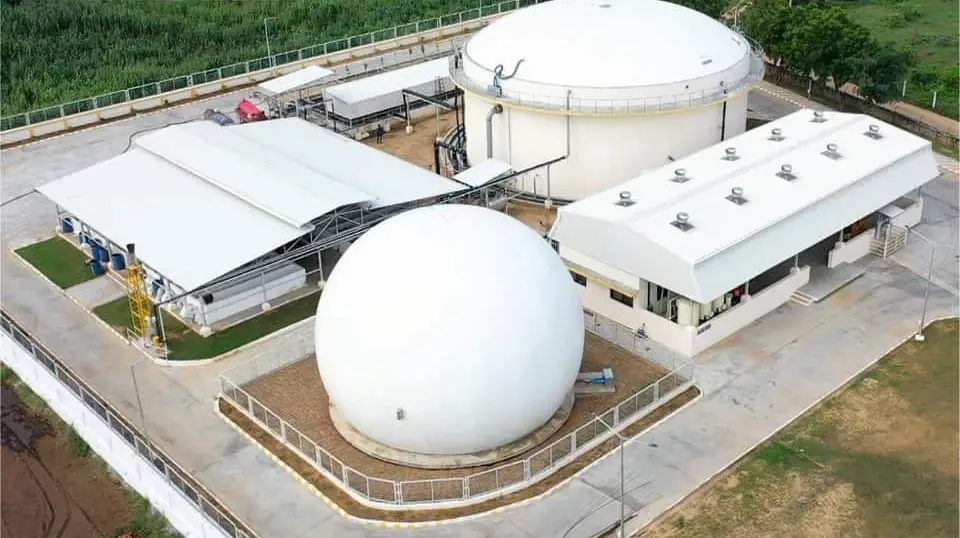
After approximately 15 months of development and construction, the very first commercial BioCNG (Compressed Natural Gas)/Biomethane plant in Indonesia has begun operations. The facility is located in Blangkahan POM, Desa Blangkahan, Kecamatan Kuala, Langkat Regency, North Sumatra.
Developed and built by PT KIS Biofuel Indonesia, the first commercial Biomethane plant in Indonesia has a Bio-CNG or Biomethane production capacity of 15,500 cubic meters per day. It is expected to reduce 3.7 million tons of CO2 annually and generate approximately 3.7 million carbon credits per year.
Noteworthy, the Blangkahan POM BioCNG/Biomethane plant is the first to be developed under a plan that seeks to develop 25 such units in the country. The 25 will have a combined production capacity of 387,500 cubic meters.
Speaking on the project Edi Wibowo, expressed his hopes for the successful operation of the first commercial Biomethane plant. He also touched on its significant contribution to supporting energy transition in the Southeast Asia and Oceania country.
Wibowo is the Director of Bioenergy at the Directorate General of New and Renewable Energy and Energy Conservation (EBTKE). The latter is under the country’s Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources.
Indonesia gets on the global Biomethane production map
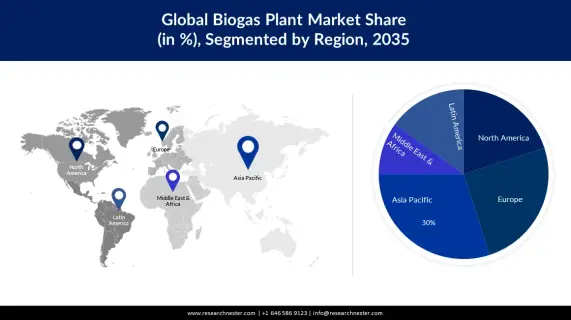
With the start of operation of the first commercial Biomethane plant in Indonesia, the country joins other countries that have embraced commercial BioCNG (Compressed Natural Gas)/Biomethane. Europe is reportedly the largest producer of biogas in the world with over 20,000 biogas plants.
The second-highest-producing region is relative. China, where national policies have led to a spread of household-scale digesters, could be ranked as the second-largest producer of biogas. The USA could also be ranked as the second-largest biomethane producer based on landfill gas recoveries and a much larger focus on upgrading to biomethane.
Other leading production hotspots across the world include Thailand from cassava waste, India from municipal waste, Brazil from landfills, and Argentina from agricultural waste. Nonetheless, most countries across the world have strong potential to produce biogas and biomethane owing to the range of potential feedstocks for production.
Measures put in place to support the adoption of BioCNG/Biomethane in Indonesia
The Indonesian government has reportedly formulated targets, strategies, and gradual and rapid programs for the use of renewable energy through various documents and policies. This, According to Wibowo, is in a bid to support energy transition in the country.
Particularly, in favour of BioCNG/Biomethane adoption, the government through the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources has devised the Grand National Energy Strategy (GSEN). This strategy seeks to reduce dependence on fossil energy consumption via the adoption of large-scale BioCNG for industries as a replacement for LPG.
The ministry has also undertaken various efforts, including issuing the SNI 9164 Biometane for Fuel in 2023 with BSN. Other measures that the ministry has taken are initiating the go-live and launching of the Business Licensing for KBLI (Indonesian Business Standard Classification) 35203 biogas procurement.
Moreover, the ministry is overseeing the licensing of biogas as a fuel with the Ministry of Investment/BKPM. It has also collaborated with several partners for BioCNG plant construction, pre-feasibility studies, economic studies, trade policy studies, and BioCNG raw material studies.
Also Read
Construction for Götene biogas plant in Sweden commences
BTS Biogas consolidates its presence on the French market with the construction of two new plants
