Preserving high-value historic buildings through Building Restoration is a crucial endeavour that demands exceptional skills. Let’s explore this process details.
The restoration of a historic building involves the meticulous task of returning it to its original state and it needs profound knowledge of past construction techniques and materials. To ensure the preservation of a building’s heritage, architects must adhere to conservation principles, avoiding irreparable damage in some cases.
To facilitate this process, the Italian company ACCA software has designed Edificius, the HBIM historic buildings software and the most advanced 3D modelling technology applied to the conservation, protection and recovery of existing buildings as well as historic and monumental buildings. It is used for creating surveys of existing buildings, modelling heritage preservation works, and representing typical heritage degradation zones.
Let’s discover what is HBIM, the various aspects of a restoration project and how Edificius can help the enhancing process of the cultural heritage.
What exactly is HBIM (Heritage Building Information Modelling)?
The acronym HBIM stands for Heritage Building Information Modelling, a term that signifies the application of the Building Information Modelling (BIM) methodology to various aspects as the listed below:
- modelling of historic buildings;
- damage and decay area surveys management;
- assisted planning tools for restoration, recovery, protection, conservation and maintenance of existing heritage assets.
Standard procedure for the restoration of historic buildings
A historic building’s restoration process unfolds through various phases, encapsulated in the following steps:
- historic building’s survey and diagnosis of degradation phenomena: this first stage includes a thorough examination of the historic building and the diagnosis of any degradation phenomena that may be present; in this phase the use of an HBIM (Historical/Heritage BIM) software facilitates the digital documentation and reporting of the current condition of the property;
- historical studies and analysis of construction techniques or materials: the next step includes an in-depth investigation of historical data as well as material or technique analysis; during this stage, a variety of documentation, including pictures, blueprints, and technical drawings, must be gathered and integrating a BIM management system (usBIM) becomes essential;
- designs for restoration and recovery interventions: once the preliminary studies are successfully concluded, the focus shifts to the formulation of specific designs for restoration and recovery interventions;
- restoration and interventions’ works: the implementation of the planned intervention takes place at this stage and particular attention is paid to safety aspects, both for the ongoing work and for those involved; that’s why the use of health and safety BIM software (CerTus HSBIM) is essential to ensuring a safe working environment;
- final documentation and restoration’s monitoring: upon the completion of all restoration and intervention works, it is essential that documentation is carefully catalogued and archived; this involves creating a comprehensive record of all restoration-related documents and using online solutions that enable the secure storage and accessibility of documents at any given time.
Edificius: the innovative software for the digitization of existing and historical building heritage (HBIM)
ACCA software, the Italian leading developer of BIM solutions for the AEC industry, has specifically designed Edificius, the most advanced 3D modelling software technology applied to the conservation, protection and recovery of existing buildings and historic and monumental buildings.
The HBIM historic buildings software Edificius allows professionals to create 3D digital models of the building starting from the survey with point clouds or from DXF/DWG/IFC drawings and models.
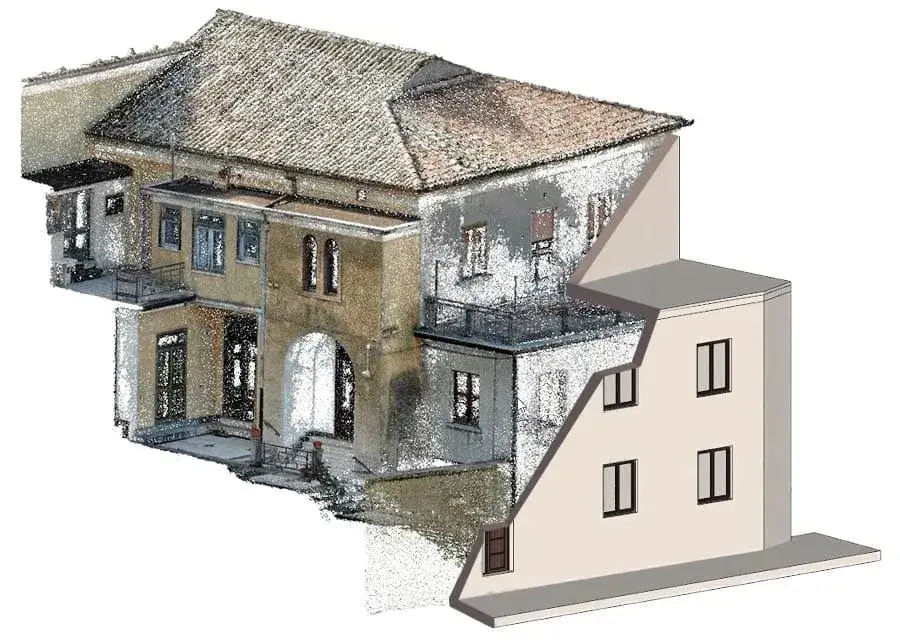

The software makes building restoration easier and more intuitive by providing a variety of utilities, including the listed below:
- modelling different types of vaults and domes and insertion of vault ribbings;
- modelling of the wooden floors down to the smallest detail;
- drawing of architectural and decorative elements of any kind;
- reproduction of niches with all the characterized elements;
- association of orthophotos to the building elements to reproduce realistic façades elevation mapping;
- identification and recreation of damage and decay areas.
Once the HBIM model is completed, the software automatically generates the project documentation (plans, sections, elevations, etc.), isometric views, working drawings, dynamic cost estimates, photorealistic renderings.
In the end, thanks to the integration with the BIM management system usBIM, professionals can manage and share the HBIM model online and take advantage of a series of benefits of the cloud as the listed below:
- geolocation of the digitized historic building with thematic GIS maps (BIM GIS softwaregis);
- access to all data, documents and models from anywhere using any device;
- browsing and federation of 3D models from a simple web browser;
- collaboration with other professionals in real time with online instant messaging, video meetings, etc.;
- storage, connection and collaboration of all survey files in a single sharing environment together with graphical and descriptive drawings, technical datasheets with degradation analysis, crack patterns, restoration interventions, project drawings, etc.
See how Edificius works for the digitization of existing and historical building heritage (HBIM)!
In the following video you can see an example of HBIM project the “Monte Monumental Complex” (situated in Montella, province of Avellino, Campania Region, Italy).
