Utility mapping is an essential procedure when it comes to commercial construction. The journey of a thousand miles began in Boston in November 1896 with a single step of initiating a 3D map to cater for the surface and subsurface construction.
Since the streets were busy and congested, a burning sensation pushed Boston to implement the idea of Ground-penetrating Radar (GPR) and the Electromagnetic location (EML) to secure the movement of people under the streets.
The idea was fantastic, and that’s how the designing, planning, and construction of the most remarkable American subway came to exist. Despite the success of the subway structure, there were a lot of challenges. For example, the building buried utilities to provide a framework to support subsurface in infrastructure.
In addition, there was an inefficiency in the accuracy of the subsurface infrastructure maps. For any underground construction to succeed, there’s a need to invest in versatile tools like electromagnetic location that can help in oil tank locating, utility mapping, and concrete scanning to detect high voltage cables implanted in the slabs.
Without proper verification of subsurface utilities, it won’t take long before a pipeline gets damaged by exposure to heavy machines, which may risk the public’s safety and hinder service; Hence, the emphasis of subsurface utility engineering (SUE).
What is Utility Mapping?
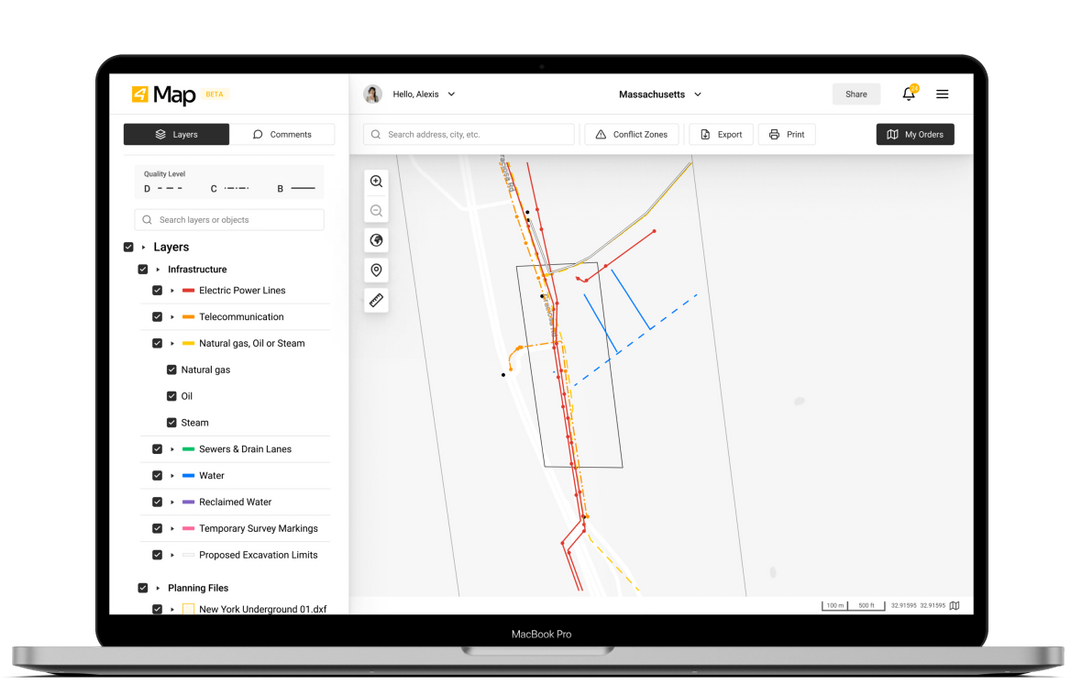
Utility mapping is the application of the latest technology that involves the drawing of sketches and charts. It ensures easy identification of cable routes and conduits underneath the soil’s surface by using a high-end combination of invasive and non-invasive tools to characterize sub-surface construction.
Utility mapping is standard, especially in the surveying, engineering, and architectural sectors. 3D Mapping assists in detecting sewers, electrical cables, sharp interfaces between the slabs, telecom cables, natural gas, water mains, shafts, and other infrastructure.
Why the Need For Mapping?
Mapping is mandatory, especially when it comes to the enforcement of the Health and Safety guidance of the UK, which doesn’t give a chance to the bad rubbish of ignorance. The guidelines are crystal clear that there’s a need for cross-checking and thorough planning before embarking on any groundwork. Here’s why:
- To meet the company’s requirement under the Construction Design and Management Regulations (CDM) and the Health and Safety UK act. It helps in safeguarding the general public and also the safety of laborers.
- It helps to stay clear of re-rerouting of utilities done in the bare construction stage; Hence, it helps to cut down on unexpected project costs and saves on downtime.
- It spots dangerous conditions. Construction is a hazardous activity itself to undertake. Several misfortunes may occur, be it to the structures, the workforce team, or the people surrounding the construction site. The accidental effects are fatal. Utility mapping comes in handy as it helps avoid calamities by laying a foundation for planning and construction.
Utility Mapping Techniques
Top-notch infrastructure engineers who are qualified for any construction work will ensure they are well conversant with modern technology to satisfy their clients. By keeping up with modernity, here are some techniques used when mapping utilities.
Electrical Method
Electrical mapping methods involve the pathway in which current electrodes directly contact a prominent conductor—the conductor used in usually metal or an ore body.
Electric currents may not necessarily come from ore or metal materials since the earth also releases its natural currents from various origins in the form of electromotive forces. These forces are transformed into electrochemical and electrokinetic energy from the fountains.
Ground Penetrating Radar
Ground Penetrating Radar is a geophysical method of mapping. The tool is used to detect electromagnetic concrete. It usually contains transmitting and receiving antennas that send signals and dictate magnetic waves at limited amplitude and frequencies.
GPR helps detect subsurface debonding between the FRP bridge deck and delaminations. GPR has a more penetrating power than other techniques, thus detecting concrete irregularities in depth.
GPR works better in scanning water debonding but not air-filled debonding. Other techniques used in mapping include; Electromagnetic method, potential-based method, direct method, an electromagnetic method, and multisensory technology.
Mapping helps manage and minimize the risks involved in site’s overruns costs and schedule delays that may be caused by inconveniences in engineering feat and ignorance when it comes to lack of proper analysis.
When building any structure, it is crucial to adhere to the rules and regulations of the public’s health and safety guidelines, the owner’s liability, and the rights of other entities that may have the legal right of the land ownership in relation to the project that is being executed. Choose a company that is attentive to detail. They should have all the necessary factual data from credible sources rather than relying on unreliable sources whose information and standard quality aren’t up to date. Furthermore, they should also possess licenses and agreements. With all these in mind, the investigations would be complete.