Italian oil and gas contractor, Saipem, has been awarded a €520 million contract by Eni for UK’s Liverpool Bay Carbon Capture Storage (CCS) project. The Engineering, Procurement and Construction (EPC) contract is for 3 years, by when the Liverpool CCS project will be complete. United Living Energy Limited was also awarded a 3 years £250 million contract. Their role has been described as a primary contractor for the Liverpool Bay CCS project.
Project factsheet
Owner: Liverpool Bay CCS Limited
Location: Liverpool Bay, UK
Developer: Eni
Project partners: Encyclis, EET Viridor, Heidelberg Materials, Progressive Energy
EPC contractor: Saipem
Saipem EPC contract cost: €520 million
Project start date: 2020
Current status: Construction
Start of construction: 2025
Project completion date: 2028
Saipem’s €520 Million EPC Contract and the Project’s Construction Phase
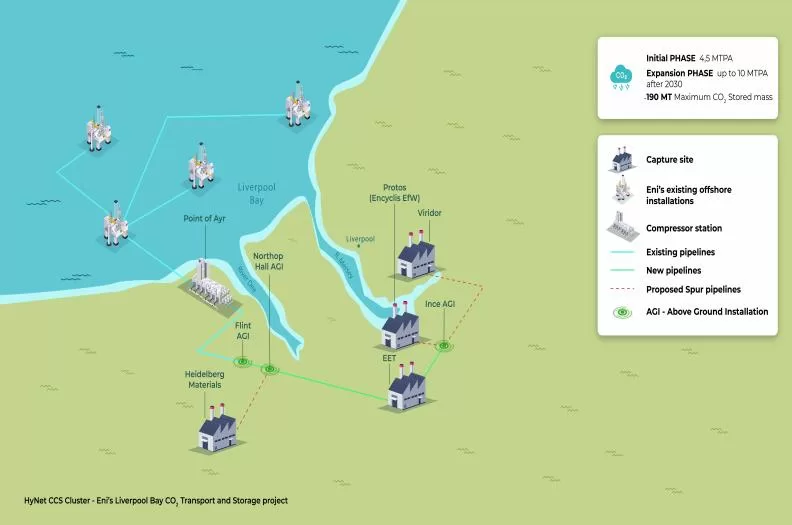
Saipem’s EPC contract for the CCS facility in Liverpool Bay is aimed at developing a compression station. This will involve the conversion of the existing gas compression and treatment facility at Point of Ayr, in north Wales into a CO2 compression station.
The electrical CO2 compression station will allow for permanent carbon storage in the Liverpool Bay area which currently houses depleted offshore sites. Additionally, the €520 million EPC contract will also include development in both offshore and onshore segments of the Liverpool Bay CCS compression station.
Saipem’s EPC contract for the development of the Liverpool Bay CCS compression station will also include project commissioning. This will feature assistance to commissioning of the new facility in 2028.
The project’s construction phase will also include changes to parts of the offshore platforms, as well as 149km of onshore and offshore pipelines. Also included in the construction plans is the installation of 35km of new pipelines to connect industrial CO2 emitters to the Liverpool Bay CCS network. These emitters include cement manufacturers, waste plants, and low-carbon hydrogen producers, among others.
The Liverpool Bay Carbon Capture Storage (CCS) Project
Eni, an energy company driven by a philosophy to support “socially fair energy transition” globally, runs the Liverpool Bay Transport and Storage infrastructure.
Liverpool Bay Carbon Capture Storage network sits in the HyNet North West Industrial Decarbonisation Cluster. The cluster is made up of industries in the North West of England and North Wales.
Upon CO2 transport to the carbon capture storage facility in the Liverpool Bay area, the green-house undergoes changes, among them compression, before storage. Storage in Liverpool’s HyNet CCS cluster is done in the depleted natural gas reservoirs lying offshore.

Benefits of the Liverpool Bay CCS Project
The project is driven by two main objectives. These are achieving Net Zero and supporting the UK’s economic growth. The Liverpool Bay CCS facility will also make the HyNet North West one of the world’s first low-emission industrial clusters. The industrial cluster is also one of the UK’s most energy-intensive manufacturing districts.
Net Zero Goal By 2030
Since the CCS project inception in October of 2020, the project has seen tremendous progress. This also includes the government granted permission to transport CO2 in March 2024. Currently, the UK has a target of storing up to 30 million tons of CO2 by 2030. This initiative is plainly underscored by the government’s £21.7 million pledge to support the development of CCS projects in the UK in October last year.
Currently, the Liverpool Bay CCS facility is in its initial phase with an initial target capacity of 4.5 million tons per annum (MTPA). This number is expected to increase to 10 MTPA after 2030. In the long-run, this will effectively lead to the storage of a maximum of 190 metric tons (MT) of CO2.
Economic Support
The CCS project is in itself geared towards economic development. This is achieved by the investments channeled to the transport and storage of CO2. This then creates another chain of new jobs in the thousands, which the project developer, Eni, puts at 2,000 in the construction phase alone.
The EPC project by Saipem will also use more than 1,000 local resources during the construction phase. This was also emphasized by Eni less than a week ago after the project reached financial closure, and marking the start of the construction phase.





